The requirements of mold design and production are: accurate size, smooth surface; reasonable structure, high production efficiency, easy to automate; easy manufacturing, high life, low cost; design meets the needs of the process, economical and reasonable.
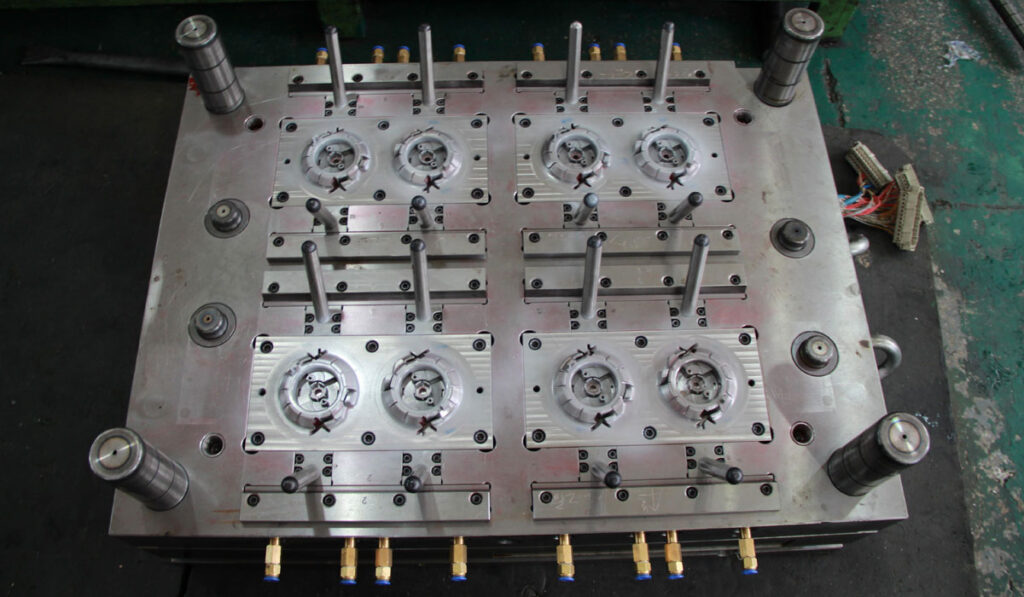
The mold structure design and parameter selection must consider factors such as rigidity, guidance, unloading mechanism, positioning method, and gap size. The wearing parts on the mold should be easy to replace. For plastic molds and die-casting molds, it is also necessary to consider a reasonable pouring system, the flow state of molten plastic or metal, and the position and direction of entering the cavity. In order to improve productivity and reduce the loss of runner pouring, a multi-cavity mold can be used, and multiple identical or different products can be completed in one mold at the same time. High-efficiency, high-precision, and long-life molds should be used in mass production.
The stamping die should use a multi-station progressive die, and a cemented carbide insert progressive die can be used to increase the life. In small batch production and trial production of new products, simple molds with simple structure, fast manufacturing, and low cost should be used, such as combined die, sheet die, polyurethane rubber die, low melting point alloy die, zinc alloy die, superplastic alloy die, etc. Molds have begun to use computer-aided design (CAD), that is, to optimize the design of molds through a set of computer-centric systems. This is the development direction of mold design.
According to structural characteristics, mold manufacturing is divided into flat punching molds and cavity molds with space. The punching die uses the convex die and the concave die to accurately match the size, and some even have a gapless fit. Other forging dies such as cold extrusion dies, die-casting dies, powder metallurgy dies, plastic dies, rubber dies, etc. are all cavity dies and are used to form three-dimensional workpieces. The cavity mold has size requirements in the three directions of length, width, and height, and the shape is complex, making it difficult to manufacture. Mold production is generally single-piece, small-batch production, with strict and precise manufacturing requirements, and most use precision processing equipment and measuring devices.
The plane blanking die can be formed by electrical discharge machining, and then formed by forming grinding, coordinate grinding and other methods to further improve the accuracy. Forming grinding can be done with an optical projection curve grinder, or a surface grinder with a mechanism for mimicking and repairing the grinding wheel, or it can be ground with a special profile grinding tool on a precision surface grinder. The coordinate grinder can be used for precise positioning of the mold to ensure precise hole diameter and hole distance. Computer numerical control (CNC) continuous trajectory coordinate grinder can also be used to grind convex and concave dies of any curve shape. Cavity molds are mostly processed by profiling milling machines, EDM and ECM. The combined application of profiling milling and numerical control and the addition of a three-way translation head device in EDM can improve the processing quality of the cavity. Adding gas-filled electrolysis in electrochemical processing can improve production efficiency.
Link to this article:Mold Making
Reprint Statement: If there are no special instructions, all articles on this site are original. Please indicate the source for reprinting:Mold Wiki,Thanks!^^
